What is 3D Laser Scanning?
what is 3d Laser scanning?
A Brief Introduction to 3D Laser Scanning tEcnology
the basics
First and foremost, 3D laser scanning is a way to capture the world around us. It is like taking a snapshot or photo, but with depth. It is usually done for the purpose of 3d modeling. 3D laser scanning has found its way into popular culture, see in example this scene from the movie Prometheus. There is also a reality show called Time Scanners that features 3D laser scanning of architectural structures. But what is 3d laser scanning? In it’s simplest form, it is a measuring device. When you use a yard stick to measure the width of a door, you are comparing the door to a known reference (which is the tape measure obviously). Laser scanners have a known reference as well, which is the speed of light. Since the speed of light in air is a known quantity and it doesn’t change (well technical it can change with altitude but not enough to make a difference), the speed of light is our yard stick. A laser scanner sends out a pulse of light, and if the pulse hits something, it reflects light back. The scanner waits for this reflection and measures the time it takes for the reflection to come back. Once it knows the reflection time, it can calculation the distance to the object. The sensor that emits and senses these pulses is called a LIDAR sensor. Here’s an excellent video on how LIDAR works.

How did laser scanning start?
3D laser scanning is thought to have been first developed in 1992 By Mensi called the Soisic scanner. But the first commercially successful endeavor startedby in 1996 by Ben Kacyra and his company called Cyra Technologies, Inc in northern California. Here is a photo of it, not pretty at all compared to the sleek and compact scanners of today. Here is a more extensive account of its development, for interested readers. It is worth noting that Leica eventually bought Cyra Technologies in 2001. Leica is our vendor of choice, so it is interesting to note that our scanners predecessors date back to the very origin of the industry. And the industry is still young. In fact you can still buy an old Cyra scanner on Ebay as of this writing. But a little known fact is that the concept of laser scanning was actually conceived by Ridley Scott as shown in the movie Aliens with the really cool laser scanning scene.
major Evolutions of 3D Scanner models

year 1992: Soisic Scanner
First scanner commercially available. Very slow and not very good.

year 2000: CYRAX 2500
Designed for engineers and surveyors – the first commercially viable scanner. 1200 points per second

year 2004: Leica Scanstation
The first 360-degree scanner with a rotating turret. Slow but accuracy, range and speed getting better.

year 2009: Leica Scanstation C10
Range, speed, reliability and accuracy. Slower than modern scanners but data quality very good.

year 2011: Faro Focus
This compact and lower-priced model really shook up the industry.

year 2016: Leica BLK360
The world’s first “pocket” laser scanner with it’s very small size.

year 2018: Leica RTC360
Unrivaled speed and sophistication at 2 million points per second.

how does a 3d scanner work?
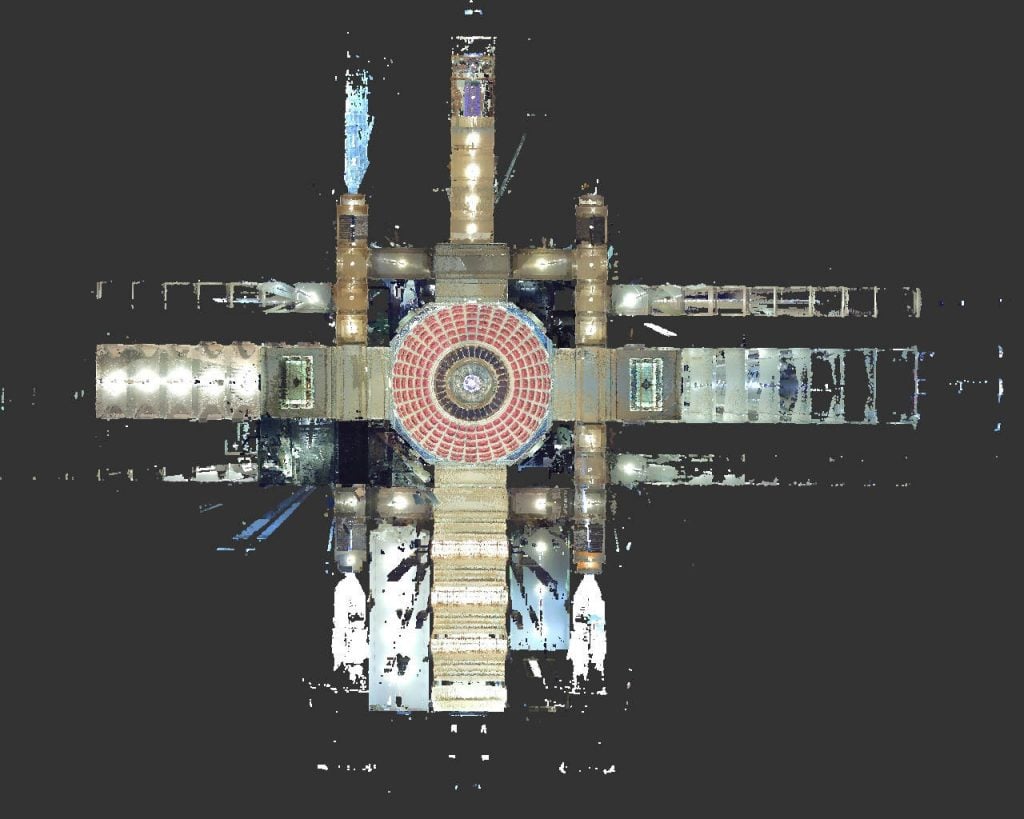
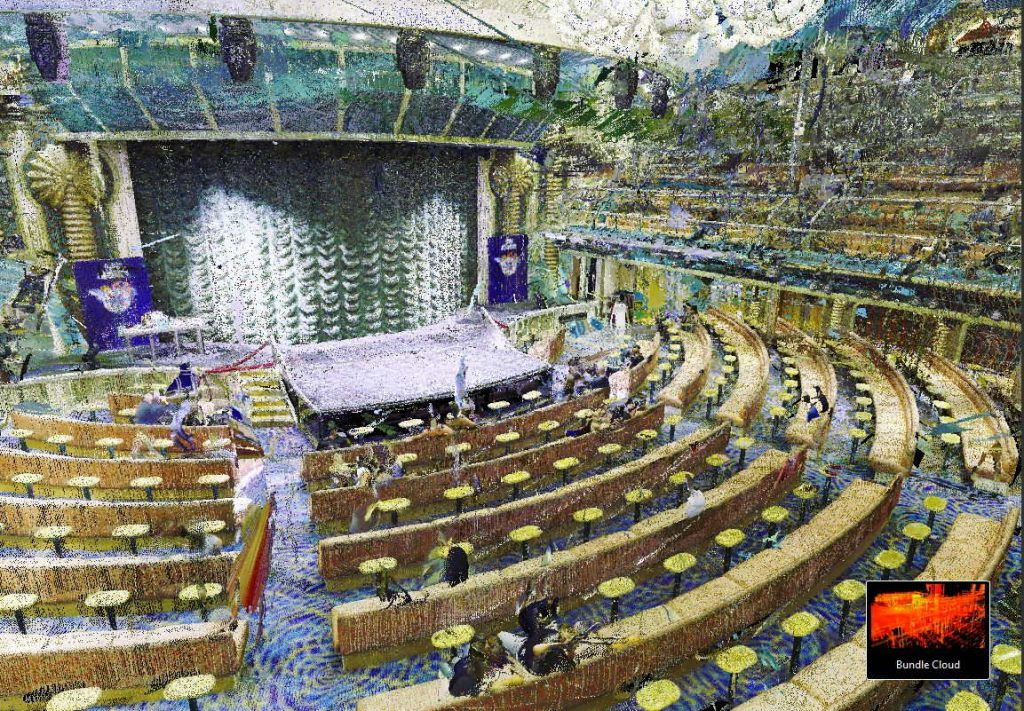
3D modern laser scanning is very simple in principle. A laser scanner is mounted on a tripod and placed within the area to be scanned. Through the use of a fast spinning mirror and rotating turret, the scanner fires a laser millions of times per second and detects the way the room reflects all of the signals it sends out, with which it can calculate a “slice” of the room. The scanner slowly rotates, systematically sweeping the room until it has a complete picture of the 3D space around it. This collection of measurements is called a point cloud. Some scanners also contain a camera, and a second 360-degree sweep is used to capture 3D photographs which can then be used to map colors onto the point cloud. This color point cloud is the data set from which we can extract valuable information and 3D models.
what is the 3d scanning process?
1. Data Acquired via Laser Scanning
We conduct the 3d scan on site, capturing as many scans as necessary to fully cover the object(s) of interest.
2. Resulting Point Clouds Registered
Each scan appears as millions of points called a “point cloud”. These point clouds are “registered’ or stitched together to create a total 3D representation of the object(s).
3. Useful Information Extracted
Using various software tools, the point cloud data is converted into the desired deliverable format. This could be 3D CAD models, animations, 2D CAD drawings, or a print-to-3D ready model.
4. Result Delivered to Customer
The final result, whether it be a CAD model or animation, is delivered to the customer in a timely manner.


who uses 3d scanning?
- Power Plant Engineers
- Facility Managers
- Architects
- BIM Managers
- Aerospace Engineers
- Mold Makers
- Machinists
- Product Designers
- Inventors
- And you!
when would one use 3d scanning services?
- You have a mold that we’ve been using for 30 years and have no drawings for it
- You need to install additional piping within an already congested space
- You are re-purposing a space and need as-built drawings
- You have a hand-made prototype and need to create drawings to manufacture it
- You need to perform a FAI (First Article Inspection)
How much can be laser scanned in a day?
This is a difficult question to answer without knowing what is being scanned, and with what end in mind. For example, we may be able to scan miles of roadway using a mobile laser scanner in a day. we also could spend an entire day on a room full of densely packed manufacturing equipment. But to give you a better idea, if we consider rather open spaces such as a warehouse, it is generally possible to scan up to 100,000 sq ft in a day. If the warehouse is filled with equipment, then it depends on how densely packed it is. if there is a lot of equipment that could go down to 25,000 sq ft a day. When talking about office and residential space, a big factor is the number of rooms. In either case, a driving factor is the level of detail required.
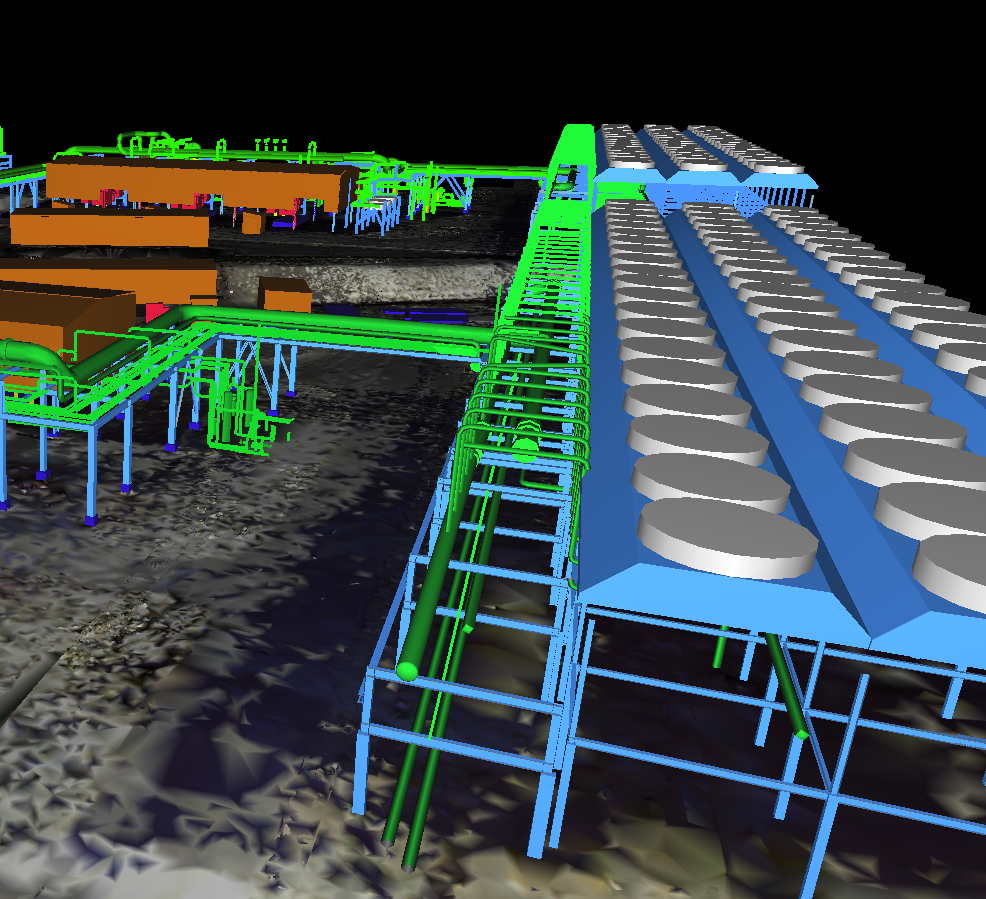

How can 3d scanning benefit me?
- Map out structure, piping and conduit to accurately plan changes to your facility
- Engineer new product prototypes
- Perform structural inspection, verifying that the structure was built as designed
- Create an as-built 3D CAD model complete with 2D drawings
- Create a BIM model for building renovation in software such as Revit
- Perform advanced space planning by make digital modifications to plant layouts by adding or removing virtual equipment
Experience Laser Scanning For Yourself
Capture your facility with incredible speed and accuracy and receive a CAD model.

